Ano ang isang Reverse Osmosis Water Plant?
In today's context of increasing water shortage and water pollution, reverse osmosis water plants, as an efficient water treatment solution, have gradually attracted widespread attention.
So, what is a reverse osmosis water plant? How does it work? What are the advantages and challenges? This article will explain the reverse osmosis water plant in detail from multiple perspectives, including technical principles, practical applications, construction costs, and operation and maintenance.
What is a reverse osmosis water plant?
A reverse osmosis water plant is a facility that uses reverse osmosis technology to treat water. Its main goal is to remove dissolved salts, organic matter, microorganisms and other impurities in water through physical and chemical means to provide high-quality pure water. Reverse osmosis water plants are widely used in municipal water supply, industrial water, seawater desalination and wastewater treatment.
What is the working principle of reverse osmosis technology?
Reverse osmosis (RO) is a technology that uses a semipermeable membrane to purify water. At its core is a reverse osmosis membrane, which has a very small pore size (about 0.0001 microns) that can block most dissolved solids, bacteria and organic matter.
1. Basic principles:
Under natural conditions, water molecules diffuse from low-concentration areas through semipermeable membranes to high-concentration areas. This process is called osmosis. Reverse osmosis achieves the purpose of purifying water by applying a pressure higher than the osmotic pressure to make water molecules flow in the opposite direction, from high-concentration areas to low-concentration areas.
2. Main steps:
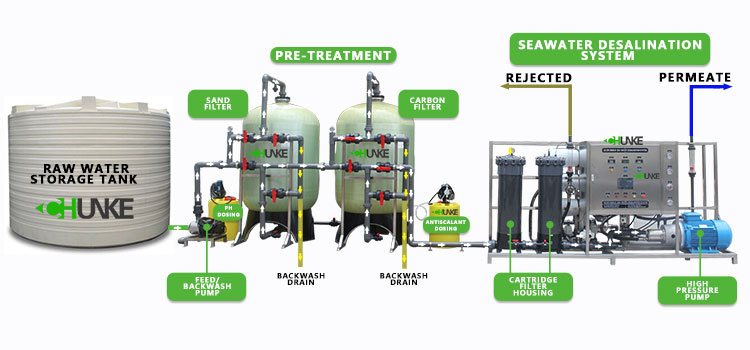
The water treatment process of a reverse osmosis water plant usually includes the following steps:
● Pretreatment: Remove suspended matter, large particles and organic matter in the water through sand filtration, activated carbon filtration and other methods to protect the reverse osmosis membrane from contamination.
● Booster pump: Pressurize the pretreated water so that it can pass through the reverse osmosis membrane.
● Reverse osmosis membrane filtration: High-pressure water passes through the reverse osmosis membrane, dissolved solids and other impurities are retained, and pure water passes through the other side of the membrane.
●Post-treatment: Adjust the pure water filtered by the reverse osmosis membrane, such as pH adjustment, mineralization treatment, etc., to meet specific water quality requirements.
● Storage and distribution: The treated pure water is stored in a water storage tank and distributed to users through a pipeline system.
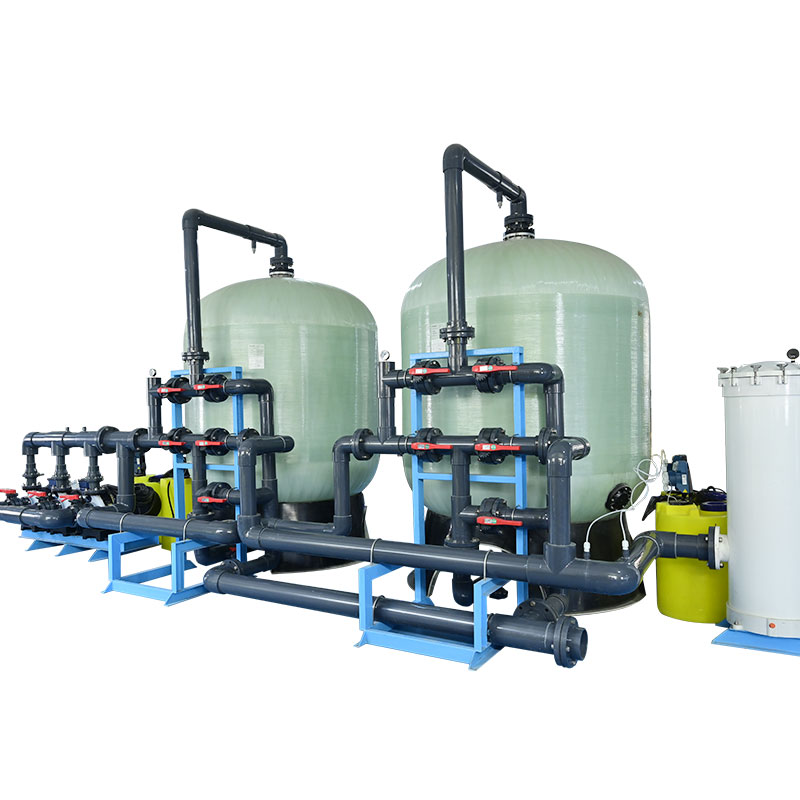

What are the practical applications of reverse osmosis water plants?
Reverse osmosis water plants have a wide range of applications in different fields, and their application scenarios mainly include municipal water supply, industrial water, seawater desalination and wastewater treatment.
1. Municipal water supply:
In some areas with poor water quality or water shortage, reverse osmosis water plants are widely used for municipal water supply. For example, countries such as Israel and Saudi Arabia use reverse osmosis technology to desalinate seawater into drinking water to provide residents with high-quality living water.
2. Industrial water:
Many industrial production processes have strict requirements on water quality, such as electronic manufacturing, pharmaceutical production and food processing. Reverse osmosis water plants can provide pure, high-quality process water to meet the needs of industrial production.
3. Seawater desalination:
Seawater desalination is one of the important applications of reverse osmosis technology. Through reverse osmosis water plants, salt and impurities in seawater are removed to produce drinkable fresh water. This technology is particularly important in coastal areas with scarce water resources.
4. Wastewater treatment:
Reverse osmosis technology is increasingly used in wastewater treatment. Through reverse osmosis water plants, industrial wastewater and municipal sewage can be effectively treated and reused, reducing pollution to the environment and saving water resources.
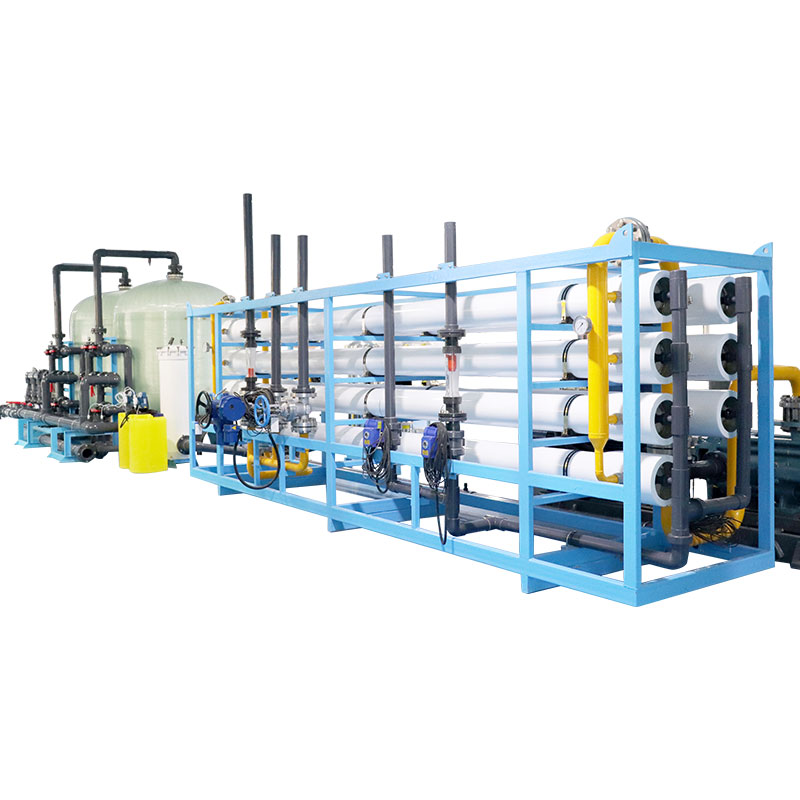

What are the costs of building a reverse osmosis water plant?
Building a reverse osmosis water plant requires consideration of multiple aspects of cost, including design cost, equipment cost, construction cost and operating cost.
1. Design cost
Design cost includes preliminary design, detailed design and process design. Professional water treatment engineers are required in the design stage to develop a reasonable design plan based on specific needs and conditions.
2. Equipment cost
Equipment cost is the main expenditure for building a reverse osmosis water plant, including reverse osmosis membrane, booster pump, pretreatment equipment, post-treatment equipment and control system. The selection and configuration of equipment directly affects the treatment capacity and water quality of the water plant.
3. Construction cost
Construction cost includes civil engineering and equipment installation costs. Civil engineering includes infrastructure, earthwork excavation and construction, while equipment installation involves equipment hoisting, installation and commissioning.
4. Operating cost
Operating cost includes staff wages, energy consumption, chemicals and daily maintenance costs. The operating cost of a reverse osmosis water plant is high, and professional personnel are required for management and maintenance.

Advantages and challenges of reverse osmosis water plants
1. Advantages:
● Efficient removal of pollutants: Reverse osmosis technology can effectively remove dissolved salts, organic matter, microorganisms and other impurities in water, providing high-quality pure water.
● Wide application: Reverse osmosis water plants are suitable for a variety of water treatment scenarios, such as municipal water supply, industrial water, seawater desalination and wastewater treatment.
● Mature technology: After years of development and application, reverse osmosis technology has become very mature and reliable, and can meet various water treatment needs.
2. Challenges:
● Waste of water resources: The reverse osmosis process will produce a certain amount of wastewater. Usually, for every liter of pure water treated, 3-4 liters of wastewater will be produced. This not only increases the waste of water resources, but may also bring additional treatment costs.
● High energy consumption: The reverse osmosis process requires high-pressure pumps to provide energy, so the energy consumption is high, which increases operating costs.
● Equipment maintenance: Reverse osmosis membranes and other equipment need to be maintained and replaced regularly. Improper maintenance may lead to system performance degradation and water quality problems.

Conclusion
As a highly efficient water treatment facility, reverse osmosis water plants can provide high-quality pure water and are widely used in municipal water supply, industrial water, seawater desalination and wastewater treatment.
Although reverse osmosis water plants have significant advantages in removing pollutants and improving water quality, they also face challenges such as water resource waste, high energy consumption and equipment maintenance.