Ano ang tatlong pangunahing problema na dulot ng desalination ng tubig-dagat?
Pagpopondo at paglalaan ng mapagkukunanKung paano makatwirang maglaan ng mga pondo at mga mapagkukunan kapag ang mga pondo at mga mapagkukunan ay limitado ay isang mahirap ding isyu. Bagama't kayang lutasin ng desalination ang problema ng kakulangan sa tubig, ang mataas na gastos nito at mga kinakailangan sa pagkonsumo ng enerhiya ay maaaring makaapekto sa paglalaan ng mga pondo at mapagkukunan para sa iba pang mahahalagang proyektong pang-imprastraktura. Halimbawa, maaaring kailanganin ng pamahalaan na gumawa ng mga trade-off sa pagitan ng mga proyekto ng supply ng tubig at iba pang mga pampublikong serbisyo (tulad ng edukasyon at pangangalagang pangkalusugan), na maaaring magdulot ng mga alitan sa lipunan at pulitika. has gradually become an important means for many coastal countries and regions to solve the problem of drinking water shortage. By removing salt from seawater, seawater desalination technology can provide reliable fresh water resources for millions of residents.
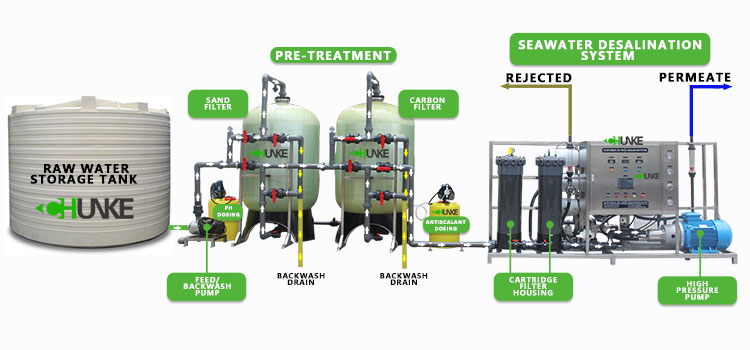
However, although seawater desalination seems to be an effective way to solve water shortages, its application process is also accompanied by some problems that cannot be ignored. This article will explore the three main problems that may arise in the process of seawater desalination: environmental impact, high energy consumption and economic cost.

Three main problems of desalination:
Issue 1 Environmental impact
● Brine discharge
● Use of chemicals
● Long-term impact on marine ecology
Issue 2 High energy consumption
● Scale of energy consumption
● Energy sources and environmental impact
● Restrictions on renewable energy
Issue 3 Economic cost
● Initial investment and operating costs
● Water prices and economic feasibility
● Funding and resource allocation

Question 1 Environmental impact
Brine discharge
In the process of seawater desalination, whether it is reverse osmosis or thermal distillation, a large amount of brine (brine) will be produced. The salinity of these brine is usually 1.5-2 times that of the original seawater, and it may also contain chemical additives, heavy metals and other pollutants. The discharge of brine (brine) produced in the process of seawater desalination is the primary problem that has a negative impact on the environment. Brine is the wastewater with high concentration of salt and other dissolved substances left after seawater has been desalinated. Because its salinity is much higher than that of natural seawater, direct discharge into the ocean will have a serious impact on the marine ecosystem.
The discharge of brine not only increases the salinity of the receiving water, but may also contain chemicals and heavy metals, such as anti-scaling agents, chlorine and other chemical additives used in the reverse osmosis process. These substances are potentially toxic to marine organisms and can disrupt the balance of the marine ecosystem, leading to the death or migration of fish and other marine organisms. In addition, high-salinity brine will change the density of seawater in the discharge area, resulting in uneven distribution of water layers, further affecting the habitat of marine organisms.
Use of Chemical Agents
In the desalination process, various chemical agents are usually required to prevent scaling of pipes and equipment. These agents include anti-scaling agents, bactericides and disinfectants. Although they play an important role in the process, their residual substances may have adverse effects on the environment and human health once they enter the marine or terrestrial environment.
For example, chlorine, as a common disinfectant, is widely used in the desalination process to kill microorganisms in seawater. However, chlorine generates harmful byproducts such as trichloromethane (THMs) in seawater. These compounds are not only harmful to marine life, but may also enter the human body through the food chain. Long-term exposure may increase the risk of cancer.
Long-term impact on marine ecology
In addition to the above-mentioned direct emissions on marine life, the long-term operation of desalination plants may also have a wider impact on the ecosystem of nearby seas. Since desalination plants are usually located in coastal areas, their water sampling ports and wastewater discharge ports are often set in nearshore areas, which are often important habitats and breeding grounds for marine life.
Long-term large-scale water extraction and discharge may cause changes in the physical and chemical properties of nearshore waters, further affecting local fishery resources and biodiversity. In addition, the operation of desalination plants may also increase noise pollution and light pollution in the surrounding areas, further disrupting the behavior patterns of marine life.
Problem 2 High energy consumption
The scale of energy consumption
Another major problem with seawater desalination is its high energy consumption. Whether through reverse osmosis technology or thermal distillation technology, the desalination process consumes a lot of energy. Reverse osmosis technology relies on high-pressure pumps to push seawater through a semipermeable membrane to remove salt, while thermal distillation requires heating and evaporating seawater and then condensing the steam into fresh water. Both processes require huge energy inputs. For example, the energy consumption of a reverse osmosis desalination system is usually between 3-4 kWh per cubic meter of fresh water, while the energy consumption of thermal distillation technology is higher, which may reach 10-15 kWh per cubic meter. Because seawater contains a large amount of dissolved salt and other impurities, it is difficult to desalinate seawater, which further increases energy consumption.
● Reverse osmosis technology: This is the most common method of seawater desalination. Its core is to use high pressure to squeeze seawater through a semipermeable membrane to achieve desalination. In order to overcome the osmotic pressure, the reverse osmosis system usually needs to apply a pressure of up to 60-80 bar, which means a lot of electricity consumption. According to statistics, reverse osmosis desalination consumes an average of 3-4 kWh of electricity for every cubic meter of fresh water produced.
● Thermal distillation technology: including multi-stage flash distillation (MSF) and multi-effect distillation (MED). These technologies evaporate seawater by heating it and then condense it into fresh water. The energy consumption of the thermal distillation process mainly comes from thermal energy. On average, it takes about 10-15 kWh of electricity equivalent thermal energy to produce one cubic meter of fresh water.
Energy sources and environmental impact
High energy consumption not only increases the operating cost of desalination, but also puts additional pressure on the environment. Most desalination plants rely on fossil fuels for electricity generation, and the combustion of fossil fuels releases large amounts of greenhouse gases and pollutants such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. The emission of these gases not only exacerbates global climate change, but also leads to deterioration of air quality, which in turn affects human health and the stability of the ecosystem.
In addition, some regions may have to increase power generation capacity to meet the energy needs of desalination plants due to insufficient energy supply, which further exacerbates the tension of energy resources and environmental pollution.
Renewable energy restrictions
Although some desalination plants have begun to explore the use of renewable energy (such as solar and wind energy) to reduce energy consumption and environmental impact, the application of renewable energy is still limited due to technical and economic limitations. For example, the efficiency of solar desalination systems is limited by climate conditions and geographical location, while the use of wind energy requires large-scale infrastructure investment. These factors limit the widespread application of renewable energy in the field of desalination.

Question 3 Economic Cost
Initial Investment and Operating Costs
The economic cost of desalination is an important factor limiting its widespread application. Building a desalination plant requires huge initial investments, including land acquisition, equipment procurement, pipeline construction, and related infrastructure construction. These initial investments usually range from hundreds of millions to billions of dollars, depending on the size of the plant and the technology selected.
In addition to the high initial investment, the daily operating costs of desalination are also very high. Operating costs include energy costs, chemical procurement costs, equipment maintenance costs, and human resources costs. Since desalination is highly dependent on equipment and technology, any equipment failure or technology upgrade may result in additional operating expenses.
Water Prices and Economic Feasibility
The high cost of desalination will eventually be reflected in the water price. Compared with traditional surface water or groundwater supply, the cost of desalinated water is much higher, which may be unaffordable for some economically disadvantaged regions. For example, in some Middle Eastern countries, the cost of desalinated water may reach 1-2 US dollars per cubic meter, which may be difficult to promote in developing countries.
In addition, the economic feasibility of desalination projects is also affected by many factors, including energy prices, chemical costs, labor costs and changes in market demand. Fluctuations in any of these factors may affect the profitability of desalination projects and thus their long-term sustainability.
Funding and resource allocation
How to reasonably allocate funds and resources when funds and resources are limited is also a thorny issue. Although desalination can solve the problem of water shortage, its high cost and energy consumption requirements may affect the allocation of funds and resources for other important infrastructure projects. For example, the government may need to make trade-offs between water supply projects and other public services (such as education and health care), which may cause social and political disputes.
Bilang karagdagan, ang pagiging posible sa ekonomiya ng mga proyekto ng desalination ay apektado din ng maraming mga kadahilanan, kabilang ang mga presyo ng enerhiya, mga gastos sa kemikal, mga gastos sa paggawa at mga pagbabago sa demand sa merkado. Ang mga pagbabagu-bago sa alinman sa mga salik na ito ay maaaring makaapekto sa kakayahang kumita ng mga proyekto ng desalination at sa gayon ang kanilang pangmatagalang pagpapanatili.